The Web Speech API is used to incorporate voice data into web apps. In this tutorial, we will build a simple webpage that uses the Web Speech API to implement text to speech. You can check the browser compatibility for the Web Speech API here.
Prerequisites
To follow along with this tutorial, you should have:
A basic understanding of HTML and JavaScript.
A code editor. I'll be using Visual Studio Code.
A browser to view the webpage, preferably Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox.
Project directory
Create a new directory for the project and create two new files called index.html and textToSpeech.js.
project-directory/
|-index.html
|-textToSpeech.js
The HTML page
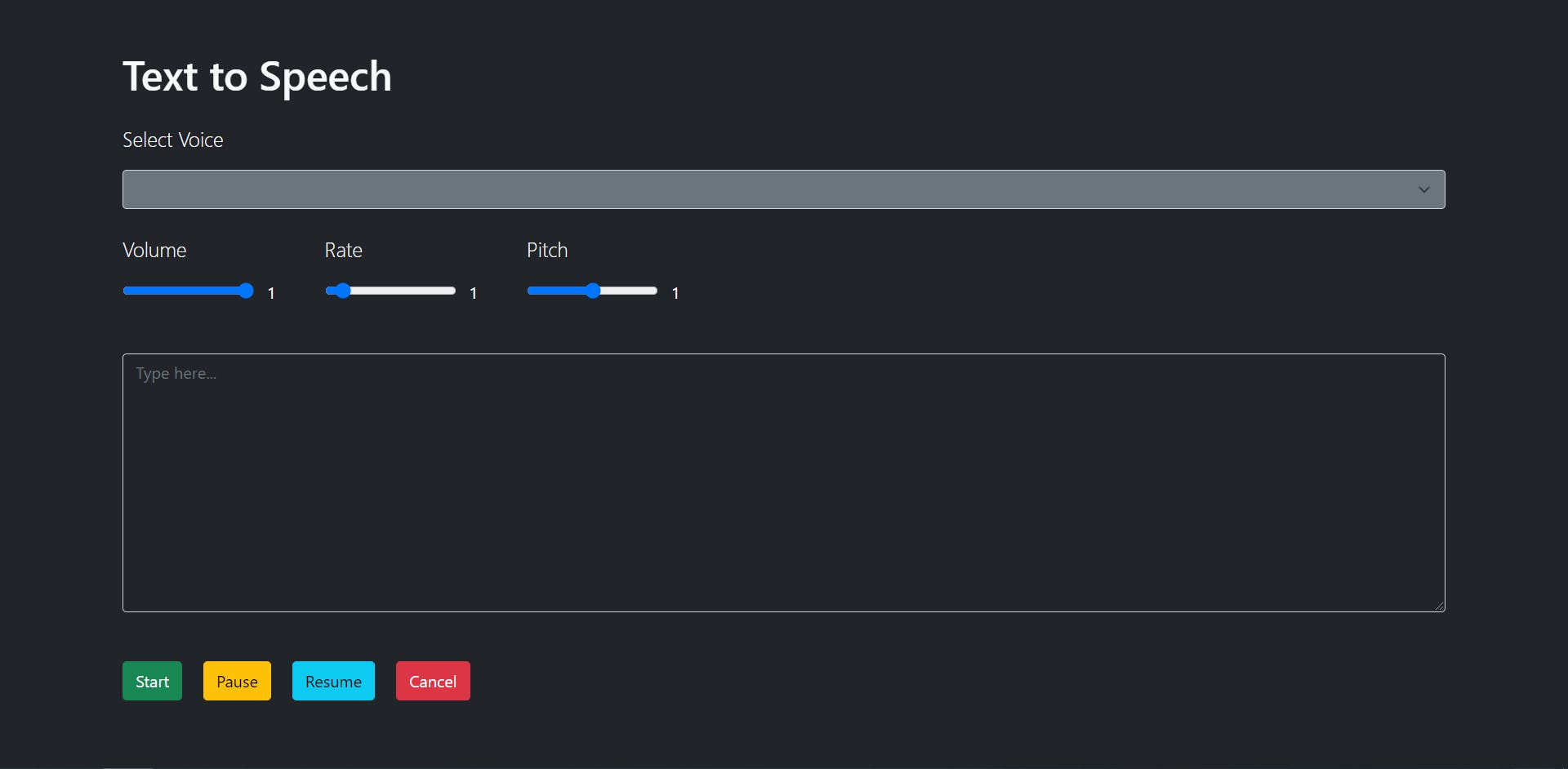
In the HTML file, let's set up:
An empty select menu. We will fill the empty select menu with the list of voices available using JavaScript.
Range sliders for volume, pitch, and rate.
A
textareato type in.Control buttons for the speech.
I've used Bootstrap 5 to style the webpage. If you are new to Bootstrap, check out their documentation to get a better understanding.
<html lang="en">
<head>
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.0.0-beta1/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="index.css" />
<title>Text to Speech</title>
</head>
<body class="container mt-5 bg-dark">
<h1 class="text-light">Text to Speech</h1>
<p class="lead text-light mt-4">Select Voice</p>
<!-- Select Menu for Voice -->
<select id="voices" class="form-select bg-secondary text-light"></select>
<!-- Range Slliders for Volume, Rate & Pitch -->
<div class="d-flex mt-4 text-light">
<div>
<p class="lead">Volume</p>
<input type="range" min="0" max="1" value="1" step="0.1" id="volume" />
<span id="volume-label" class="ms-2">1</span>
</div>
<div class="mx-5">
<p class="lead">Rate</p>
<input type="range" min="0.1" max="10" value="1" id="rate" step="0.1" />
<span id="rate-label" class="ms-2">1</span>
</div>
<div>
<p class="lead">Pitch</p>
<input type="range" min="0" max="2" value="1" step="0.1" id="pitch" />
<span id="pitch-label" class="ms-2">1</span>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Text Area for the User to Type -->
<textarea class="form-control bg-dark text-light mt-5" cols="30" rows="10" placeholder="Type here..."></textarea>
<!-- Control Buttons -->
<div class="mb-5">
<button id="start" class="btn btn-success mt-5 me-3">Start</button>
<button id="pause" class="btn btn-warning mt-5 me-3">Pause</button>
<button id="resume" class="btn btn-info mt-5 me-3">Resume</button>
<button id="cancel" class="btn btn-danger mt-5 me-3">Cancel</button>
</div>
</body>
<script src="./textToSpeech.js"></script>
</html>
The JavaScript file
Let's create an instance of the SpeechSynthesisUtterance class. We'll configure this instance with various properties.
let speech = new SpeechSynthesisUtterance();
Properties
Now, let's configure some properties on this SpeechSynthesisUtterance instance.
There are six properties on the SpeechSynthesisUtterance instance that we can tweak.
They are:
Language:
The language property gets and sets the language of the utterance. If unset, the <html lang="en"> lang value will be used, or the user-agent default if the <html lang="en"> lang is unset.
It accepts a DOMString representing a BCP 47 language tag.
speech.lang = "en";
Text:
The text property gets and sets the text that will be synthesized when the utterance is spoken. The text can be provided as plain text. In our case, the text property must be set when the start button is clicked.
Let's add a click listener to the button. When the button is clicked, we should get the text value from the textarea and set it to this property.
You can learn more about event listeners here.
document.querySelector("#talk").addEventListener("click", () => {
speech.text = document.querySelector("textarea").value;
});
Volume:
The volume property gets and sets the volume of the utterance. It is a float that represents the volume value, between 0 (lowest) and 1 (highest). The default value is 1 if this property is unset.
Let's add an onInput listener to the volume range slider and adjust the volume property when the value of the slider changes. We've already set the min, max, and default value of the slider in the HTML tag.
Let's also set the <span> that displays the value of the volume in the webpage next to the range slider.
document.querySelector("#rate").addEventListener("input", () => {
// Get rate Value from the input
const rate = document.querySelector("#rate").value;
// Set rate property of the SpeechSynthesisUtterance instance
speech.rate = rate;
// Update the rate label
document.querySelector("#rate-label").innerHTML = rate;
});
Rate:
The rate property gets and sets the rate of the utterance. It is a float representing the rate value which can range between 0.1 (lowest) and 10 (highest). The default value is 1 if this property is unset.
Let's add an onInput listener to the rate range slider and adjust the rate property when the value of the slider changes. We've already set the min, max, and default value of the slider in the HTML tag.
Let's also set the <span> that displays the value of the rate in the webpage next to the range slider.
document.querySelector("#volume").addEventListener("input", () => {
// Get volume Value from the input
const volume = document.querySelector("#volume").value;
// Set volume property of the SpeechSynthesisUtterance instance
speech.volume = volume;
// Update the volume label
document.querySelector("#volume-label").innerHTML = volume;
});
Pitch:
The pitch property gets and sets the pitch of the utterance. It is a float representing the pitch value that can range between 0 (lowest) and 2 (highest). The default pitch is 1 if this property is unset.
Let's add an onInput listener to the pitch range slider and adjust the pitch property when the value of the slider changes. We've already set the min, max, and default value of the slider in the HTML tag.
Let's also set the <span> that displays the value of the pitch in the webpage next to the range slider.
document.querySelector("#pitch").addEventListener("input", () => {
// Get pitch Value from the input
const pitch = document.querySelector("#pitch").value;
// Set pitch property of the SpeechSynthesisUtterance instance
speech.pitch = pitch;
// Update the pitch label
document.querySelector("#pitch-label").innerHTML = pitch;
});
Voice:
The voice property gets and sets the voice that will be used to speak the utterance. This should be set to one of the SpeechSynthesisVoice objects. If it is not set, the most suitable default voice available for the utterance's language setting will be used.
To set the voice of the utterance, we need to get the list of available voices in the window object. When the window object loads, the voices will not be available immediately. It's an async operation. An event will be triggered when the voices are loaded. We can set a function that should be executed when the voices are loaded.
window.speechSynthesis.onvoiceschanged = () => {
// On Voices Loaded
};
We can get the list of voices using window.speechSynthesis.getVoices(). It'll return an array of SpeechSynthesisVoice objects that are available. Let's store the list in a global array and update the select menu on the web page with the list of available voices.
let voices = []; // global array
window.speechSynthesis.onvoiceschanged = () => {
// Get List of Voices
voices = window.speechSynthesis.getVoices();
// Initially set the First Voice in the Array.
speech.voice = voices[0];
// Set the Voice Select List. (Set the Index as the value, which we'll use later when the user updates the Voice using the Select Menu.)
let voiceSelect = document.querySelector("#voices");
voices.forEach((voice, i) => (voiceSelect.options[i] = new Option(voice.name, i)));
};
Now that we have updated the voice menu, let's add an onChange event listener on it to update the SpeechSynthesisUtterance instance's voice. When a user updates the voice, we will use the index number (which is set as the value for each option) and the global array of voices to update the voice.
document.querySelector("#voices").addEventListener("change", () => {
speech.voice = voices[document.querySelector("#voices").value];
});
Controls
Let's add controls to the SpeechSynthesis instance.
Start:
We should pass the SpeechSynthesisUtterance instance to the window.speechSynthesis.speak() method when the start button is clicked. This will start converting the text to speech. The text property must be set before calling this method.
NOTE: If you start another text to speech while an instance is already running, it'll get queued behind the one that is currently running.
document.querySelector("#talk").addEventListener("click", () => {
speech.text = document.querySelector("textarea").value;
window.speechSynthesis.speak(speech);
});
Pause:
We can pause the SpeechSynthesisUtterance instance that's running at the moment using window.speechSynthesis.pause(). Let's select the pause button and add a click event listener to it and pause the SpeechSynthesisUtterance instance when the button is clicked.
document.querySelector("#pause").addEventListener("click", () => {
window.speechSynthesis.pause();
});
Resume:
We can resume the SpeechSynthesisUtterance instance that's paused at the moment using window.speechSynthesis.resume(). Let's select the resume button and add a click event listener to it and resume the SpeechSynthesisUtterance instance when the button is clicked.
document.querySelector("#resume").addEventListener("click", () => {
window.speechSynthesis.resume();
});
Cancel:
We can cancel the SpeechSynthesisUtterance instance that's running at the moment using window.speechSynthesis.cancel(). Let's select the cancel button and add a click event listener to it and cancel the SpeechSynthesisUtterance instance when the button is clicked.
document.querySelector("#resume").addEventListener("click", () => {
window.speechSynthesis.resume();
});
The final version of textToSpeech.js:
// Initialize new SpeechSynthesisUtterance object
let speech = new SpeechSynthesisUtterance();
// Set Speech Language
speech.lang = "en";
let voices = []; // global array of available voices
window.speechSynthesis.onvoiceschanged = () => {
// Get List of Voices
voices = window.speechSynthesis.getVoices();
// Initially set the First Voice in the Array.
speech.voice = voices[0];
// Set the Voice Select List. (Set the Index as the value, which we'll use later when the user updates the Voice using the Select Menu.)
let voiceSelect = document.querySelector("#voices");
voices.forEach((voice, i) => (voiceSelect.options[i] = new Option(voice.name, i)));
};
document.querySelector("#rate").addEventListener("input", () => {
// Get rate Value from the input
const rate = document.querySelector("#rate").value;
// Set rate property of the SpeechSynthesisUtterance instance
speech.rate = rate;
// Update the rate label
document.querySelector("#rate-label").innerHTML = rate;
});
document.querySelector("#volume").addEventListener("input", () => {
// Get volume Value from the input
const volume = document.querySelector("#volume").value;
// Set volume property of the SpeechSynthesisUtterance instance
speech.volume = volume;
// Update the volume label
document.querySelector("#volume-label").innerHTML = volume;
});
document.querySelector("#pitch").addEventListener("input", () => {
// Get pitch Value from the input
const pitch = document.querySelector("#pitch").value;
// Set pitch property of the SpeechSynthesisUtterance instance
speech.pitch = pitch;
// Update the pitch label
document.querySelector("#pitch-label").innerHTML = pitch;
});
document.querySelector("#voices").addEventListener("change", () => {
// On Voice change, use the value of the select menu (which is the index of the voice in the global voice array)
speech.voice = voices[document.querySelector("#voices").value];
});
document.querySelector("#start").addEventListener("click", () => {
// Set the text property with the value of the textarea
speech.text = document.querySelector("textarea").value;
// Start Speaking
window.speechSynthesis.speak(speech);
});
document.querySelector("#pause").addEventListener("click", () => {
// Pause the speechSynthesis instance
window.speechSynthesis.pause();
});
document.querySelector("#resume").addEventListener("click", () => {
// Resume the paused speechSynthesis instance
window.speechSynthesis.resume();
});
document.querySelector("#cancel").addEventListener("click", () => {
// Cancel the speechSynthesis instance
window.speechSynthesis.cancel();
});
Result
You can take a look at the project that's been deployed using GitHub Pages here.
You can also check out the final code in this GitHub Repository.
Let's recap
We created an HTML page with a select menu for the voices, a text area, and control buttons.
We created a new JavaScript file and linked it to the HTML file.
We created a new
SpeechSynthesisUtteranceobject.We tweaked the six properties of the
SpeechSynthesisUtteranceinstance. They are Pitch, Volume, Text, Voice, Rate, and Language.We added listeners on the control button to control the
SpeechSynthesisUtteranceinstance when they are clicked. They are Start, Pause, Resume, and Cancel.
Congratulations, :partying_face: You did it.
Happy Coding!
I do all my writing in my spare time, so if you feel inclined, a tip is always incredibly appreciated.

